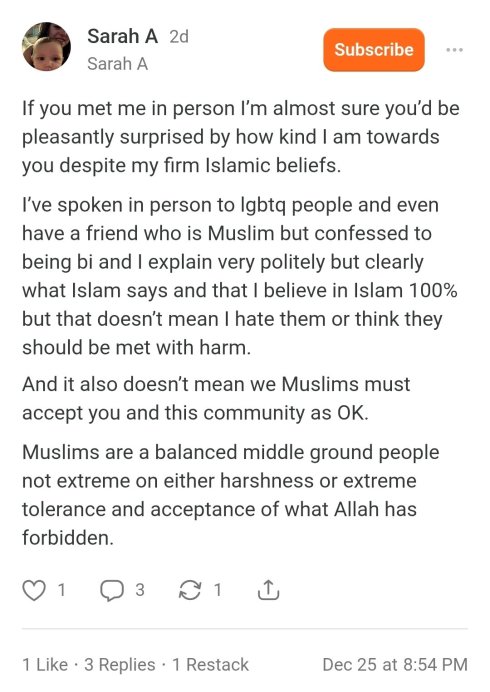
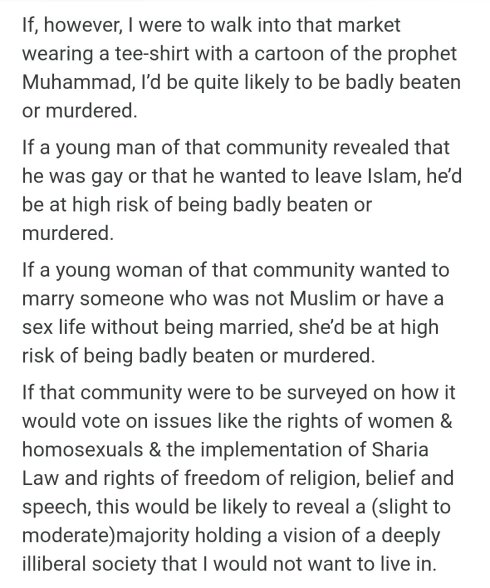
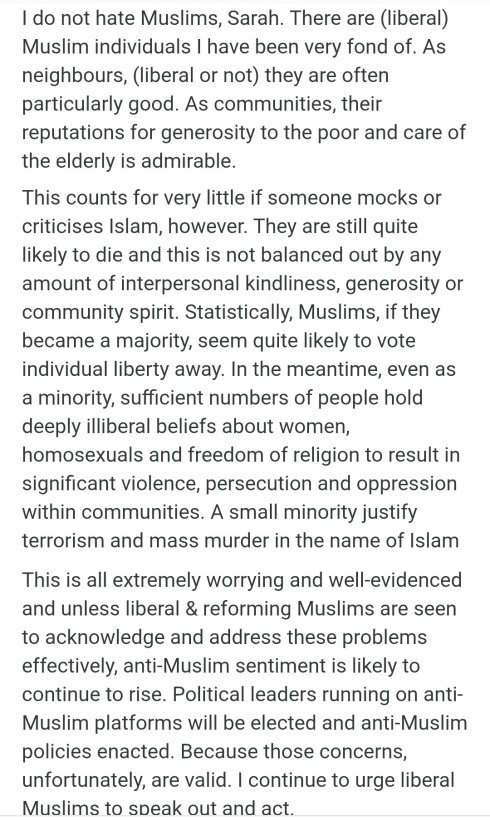
Happy New Year! “What?!”, you say, doing a reflective piece to start the new year? Unpossible!!! – Yet here we are. Take care my friends and feisty commentariate in this next orbit around the Sun.
I recently asked an LLM—Grok—to analyze Dead Wild Roses.
He obliged.
The result was thoughtful, coherent, and broadly accurate. He traced the arc of the blog from its earlier left-skeptical roots through to its present preoccupations: feminism, free speech, gender ideology, institutional capture, moral certainty. As machine readings go, it was competent. Even generous.
And yet.
Reading it, I had the distinct sense of being seen from across the room, not spoken with.
So I did what seemed obvious: I asked another model—this one—for her reading.
I’m aware, of course, that large language models are not gendered. But anyone who works with them long enough knows that they nonetheless express distinct interpretive temperaments. If Grok reads like a brisk political cartographer—mapping positions, vectors, affiliations—this model reads more like a close reader of essays, arguments, and interior continuity.
That difference matters.
What He Saw (and What He Didn’t)
Grok understood the trajectory of the blog. He recognized that this was not a sudden ideological flip but a long, incremental evolution. He correctly identified a through-line of skepticism toward authority and moral certainty.
Where his reading thinned was not in what I believe, but in how I think.
His analysis treated the blog primarily as a political object—something that moved through ideological space. That’s not wrong, but it is partial.
Dead Wild Roses was never built to advocate a position. It was built to interrogate certainty—including my own.
What I’ve Always Been Doing Here
This blog has been many things over the years: atheist, feminist, skeptical, irritated, occasionally furious. But its core method has never changed.
It asks:
-
What is being asserted as unquestionable?
-
Who benefits from that assertion?
-
What happens if we follow it all the way down?
When institutions began insisting that sex was a feeling, that language could override biology, that dissent was harm, that moral status preceded argument—the same skeptical machinery I once aimed outward turned inward.
That wasn’t betrayal.
It was consistency under pressure.
On Feminism and Material Reality
Yes, this is now read—accurately—as a sex-based feminist blog.
That’s not because identity doesn’t matter, but because material reality is the ground truth on which politics rests. Bodies come first. Law follows. Stories are last.
When political movements demand that we invert that order, something has gone deeply wrong—and feminism, if it is to mean anything at all, must notice.
That position is not reactionary. It is foundational.
Why Ask Two Models at All?
Because how something is read tells you as much about the reader as the text.
He read Dead Wild Roses as a location on a map.
She read it as a method in motion.
One isn’t false. But only one feels true.
The difference mirrors the very problem the blog keeps circling: the reduction of inquiry into identity, of thinking into stance, of method into tribe.
A Note on AI, Authority, and Voice
There is an irony here that isn’t lost on me.
I am using artificial intelligences to reflect on a body of writing that is deeply skeptical of outsourced authority. But that tension is precisely the point.
Tools can assist thinking.
They cannot replace it.
Maps can be useful.
They are not the territory.
Where This Leaves Me
If the last few years of Dead Wild Roses were about dismantling false moral certainty, the next may be about something harder and quieter:
-
rebuilding meaning without mysticism,
-
defending reality without cruelty,
-
and learning how to live after the spell breaks.
I don’t know where that road leads.
But I know why I keep walking it.
And I know which readings—human or machine—feel like they’re walking with me rather than plotting me from above.
Postscript:
Throughout this piece, I’ve used “he” and “she” to distinguish between two AI systems with markedly different interpretive styles. This is not a claim about machine ontology. It is shorthand—imperfect, human, and serviceable.
Language exists to clarify thought. When it stops doing that, it’s time to change the language—not reality.







Your opinions…